Reza Hosseini, PhD – Managing Director at RadonMarket, R&D Manager & NRPP MFM Certified Radon Professional at Niton srl
If you follow our short article series (RADON IN PILOLE 💊), you may remember that we have talked about the four main ways Radon enters buildings. Among these four, Radon coming inside buildings from gas soil due to convection has a significant 85-90% contribution role. Instead, Radon from water contributes less than 1%. Hence, Radon mitigators mainly deal with the methods to reduce the Radon coming from the soil. Still, to achieve an acceptable Radon indoor level, Radon in water should also be reduced in some cases.
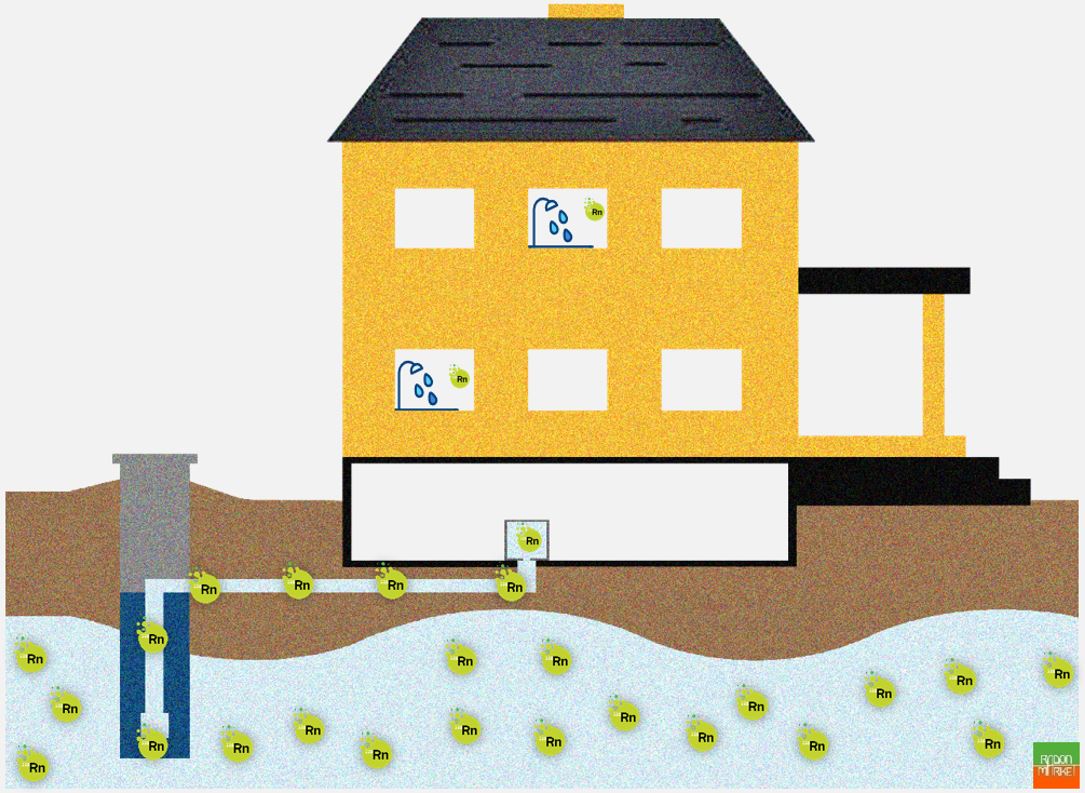
Reducing Radon in water is a complicated topic and needs skills in different areas, from plumping to water quality. We will discuss Radon in water in two numbers of RadonMarket Mag. in this number, we will see:
- How Radon goes in the water initially?
- Is the contribution of Radon in water significant?
- Notes For Radon Professionals, “What should be considered when dealing with Radon in water?”
In the next number, we will discuss the methods of Reducing Radon in water.
I. How Radon goes in the water initially?
The same Radium source that causes Radon in the gas soil could be in contact with the water in the aquifer. As Radon is very soluble in water, it can enter and dissolve easily in the aquifer. In this situation, a well that brings water from the aquifer directly to the house could also bring the Radon inside it. As the Half-life of Radon is 3.8 days, it can travel for a long distance inside the pipes and reaches even higher floors.
Radon can cause lung cancer when we breathe its decay products suspended in the air, but no evidence shows a significant health risk when we drink Radon dissolved in water. So how Radon in water could be a health risk?
If you don’t remember the health effect of Radon, watch the videos of this Free course on RadonMarket Academy.
Actually, Radon in water could be a health risk only when the dissolved Radon comes out of the water as soon as it reaches the atmospheric pressure and diffuses inside the closed area of a building. For example, it could happen when the water is used for the shower or the dishwasher. Like any other dissolved gas, Radon tends to come out of the solution at a higher temperature, for example, a shower with hot water. The Radon that comes out of the water solution then adds to the Radon coming directly from the soil (or from other sources) and increases the Radon concentration level inside the building.
II. Is the contribution of Radon in water significant?
The unit of measurement for Radon in the water is Bq/L (pCi/L in water). On average, 1000 Bq/l of Radon in the water can add 100 Bq/m3 to the overall indoor Radon level (10,000 pCi/L in water can yield around 1 pCi/L into the air). Please consider that this is an average value and could be vary based on the amount of water is used, ventilation of the building, and many other factors.
To see how we can calculate the significance of the contribution of Radon in the water compared to the overall Radon concentration inside a building, we make an example:
|
🤷 Inside a house, it measured 500 Bq/m3 of indoor Radon. A separate test is performed to measure the Radon in water, and the result shows 1500 Bq/l. What is the primary source of indoor Radon for this building? ✏ The contribution of Radon in the water is about 150 Bq/m3. ✏ Therefore the contribution of Radon coming from another source (More likely from the soil) is 350 Bq/m3. Use AppoRad to do these calculations. Read more at the end of this document! Looking at the measured values, it seems that the primary source of Radon in that building is the water supply. However, as demonstrated above, from the total 500 Bq/m3 Radon concentration, 350 Bq/m3 is from another source (more likely from the soil). |
The Radon in water could play a significant role depending on the level of Radon in the water, amount of water usage, and the level of Radon coming from other sources. Typically, reducing Radon coming from the soil gas has the most significant impact on lowering indoor Radon levels. Moreover, considering the complication of the techniques to reduce Radon in the water supply, it is always recommended to start working on the Radon in soil gas for a mitigation project.
III. Notes For Radon Professionals: What should be considered when dealing with Radon in water?
|
📝 The Radon inside a building could come from different sources, like soil, water, or emanation from building materials. Therefore, even though Radon coming from water does not represent a significant fraction of Radon in most cases, a Radon professional must consider these other possibilities. 📝 Buildings with groundwater supplies, especially homes with a private well, can have elevated Radon in well water. 📝 Radon moves by water, and it can go out of the pipes anywhere. In RADON IN PILOLE 💊 series, we mentioned that we might need to measure Radon level in higher floors for a complete diagnostic. Radon in water is one of the reasons! 📝 When the water is using in an open area like for gardening, the presence of Radon in water may not be a problem. Instead, when Radon can go out of water in a closed space and have time to be accumulated, we could consider it a health risk. 📝 Radon goes out of water when someone uses the water! Therefore the measurement in a building without occupation does not represent the contribution of Radon in water and its potential health risk. 📝 Using a continuous Radon monitor (CRM) could be very helpful to do a diagnostic. An increase in the Radon level could be detectable with these types of instruments each time hot water is used for a while. Even though it is not generally recommended to put CRMs inside the bathroom, it could not be a bad idea to use them for diagnostic purposes. |





